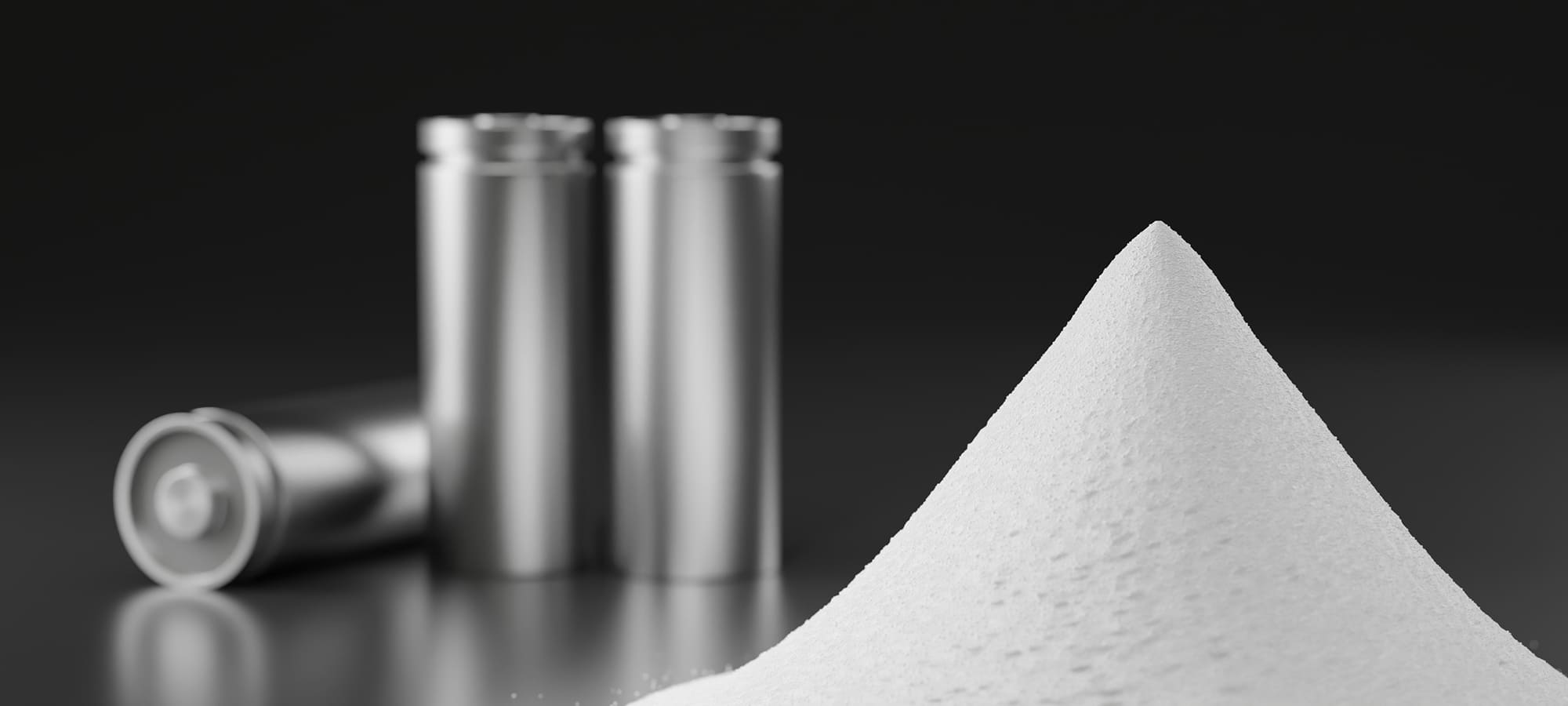

CAM and AAM are vital components in the production of lithium-ion batteries, contributing to their overall performance and efficiency.
CAM (Cathode Active Material) is the positive electrode material that stores and releases lithium ions during battery operation. Examples of CAM include lithium cobalt oxide (LCO), lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NCM), and lithium iron phosphate (LFP). Each CAM type offers unique characteristics, such as high energy density, improved safety, or enhanced thermal stability.
AAM (Anode Active Material) is the negative electrode material responsible for receiving and releasing lithium ions. Common examples of AAM include graphite and silicon-based materials. Graphite is widely used for its stability and moderate energy density, while silicon-based materials offer the potential for higher energy density, although they require careful electrode design to accommodate volume expansion during charging.
To explore the intricacies of CAM and AAM production, including the specific processes and equipment involved, and to request a quote for each machine, please contact us from the "Contact Us" page. Our dedicated team will be delighted to assist you in finding the best solution tailored to your requirements.
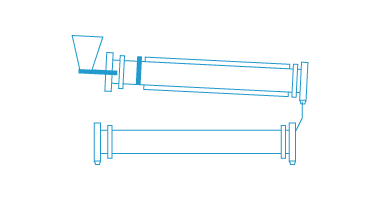
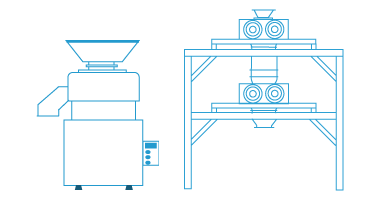
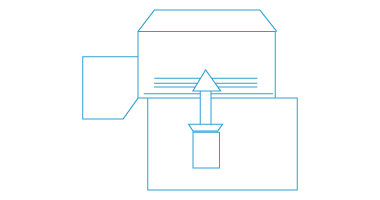

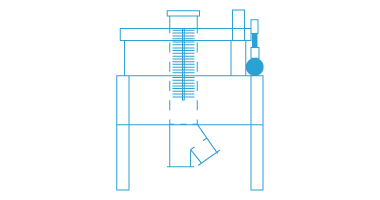
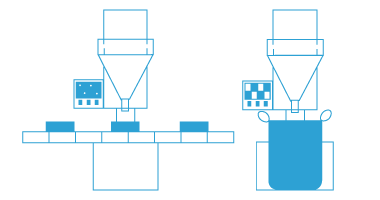
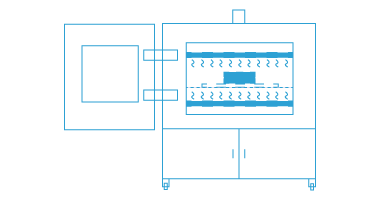

DJK also provides materials for fuel cells, especially for SOFC (solid oxide fuel cells), SOEC (solid oxide electrolyser cells).